Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Amekura, Hiroshi*; Chettah, A.*; Narumi, Kazumasa*; Chiba, Atsuya*; Hirano, Yoshimi*; Yamada, Keisuke*; Yamamoto, Shunya*; Leino, A. A.*; Djurabekova, F.*; Nordlund, K.*; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 15, p.1786_1 - 1786_10, 2024/02
Injecting high-energy heavy ions in the electronic stopping regime into solids can create cylindrical damage zones called latent ion tracks. Although these tracks form in many materials, none have ever been observed in diamond, even when irradiated with high-energy GeV uranium ions. Here we report the first observation of ion track formation in diamond irradiated with 2-9 MeV C fullerene ions. Depending on the ion energy, the mean track length (diameter) changed from 17 (3.2) nm to 52 (7.1) nm. High resolution scanning transmission electron microscopy (HR-STEM) indicated the amorphization in the tracks, in which
fullerene ions. Depending on the ion energy, the mean track length (diameter) changed from 17 (3.2) nm to 52 (7.1) nm. High resolution scanning transmission electron microscopy (HR-STEM) indicated the amorphization in the tracks, in which  -bonding signal from graphite was detected by the electron energy loss spectroscopy (EELS).
-bonding signal from graphite was detected by the electron energy loss spectroscopy (EELS).
Yamamoto, Yojiro*; Hayakawa, Sho*; Okita, Taira*; Itakura, Mitsuhiro
Computational Materials Science, 229, p.112389_1 - 112389_9, 2023/10
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:52.07(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)He bubbles are characteristic microstructures under fusion reactor conditions. They approach and coalesce through their own migration, which significantly impacts the microstructure and material properties. However, these processes, which involve multiple migrations of metal atoms, cannot be treated by molecular dynamics (MD) due to its timescale limitation. In this study, self-evolving atomistic kinetic Monte Carlo (SEAKMC) was used to expand the timescale and reproduce bubble coalescences in Fe. To enhance selections of events that led to the process by avoiding trivial events with an extremely low activation energy such as tiny vibrations of a He atom or short-range displacements of the Fe atom, we introduced two algorithms into SEAKMC, a two-step saddle point search for the former measure and setting a threshold for a displacement distance of the Fe atom for the latter. Furthermore, by adding another algorithm to set an upper bound for the activation energy to prevent selections of events with an impractically high activation energy, we succeeded to reproduce the change in the configuration from dumbbell to elliptical up to a simulated time of 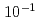 s, 8 orders longer than MD timescales. The developed method is effective for analyzing microstructures of metallic materials containing light elements and is the only method that can reach timescales comparable to those of experiments.
s, 8 orders longer than MD timescales. The developed method is effective for analyzing microstructures of metallic materials containing light elements and is the only method that can reach timescales comparable to those of experiments.
Wakui, Takashi; Yamasaki, Kazuhiko*; Futakawa, Masatoshi
Advanced Experimental Mechanics, 7, p.103 - 109, 2022/08
As part of the development of technique to cut and reduce the volume of highly radioactive components in the closed space, pulsed Nd:YAG laser was irradiated to radiation shielding glasses with the different lead content in the different irradiation condition; power and number of irradiation. The large black irradiated area with concave shape and cracks around it occurred with an increase of the lead content, power and number of irradiation. General mechanical properties in unirradiated and irradiated area were investigated to investigate the influence of mechanical properties on the irradiation damage. The thermal impact fracture toughness calculated based on the estimated mechanical properties decreased with increasing the lead content. The micro hardness in black irradiated area was 10% smaller than that in the unirradiated area. The change of the mechanical property due to the laser irradiation was confirmed.
Wakui, Takashi; Yamasaki, Kazuhiko*; Futakawa, Masatoshi
Jikken Rikigaku, 22(2), p.96 - 104, 2022/06
Pulsed laser irradiation and indentation tests on radiation shielding glasses and a lead-free glass were carried out. The size of irradiation damage of the glass with high lead content was larger than that with low content. The micro plastic behavior of glasses was quantitatively determined using the inverse analyses based on indentation results. Flow stress decreased with an increase of lead content and that in irradiated area was lower than that in unirradiated area. On the other hand, plastic flow resistance increased with an increase of the lead content and that in irradiated area was higher than that in unirradiated area. Fracture energy and critical size of plastic zone around tip of crack in unirradiated and irradiated areas were calculated based on experimental results including constants evaluated using the inverse analysis. These values decreased with an increase of the lead content and these values in irradiated area were lower than that in unirradiated area.
 superconductors
superconductorsSueyoshi, Tetsuro*; Enokihata, Ryusei*; Hidaka, Yuka*; Irie, Masahiro*; Fujiyoshi, Takanori*; Okuno, Yasuki*; Ishikawa, Norito
Physica C, 582, p.1353824_1 - 1353824_5, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:7.92(Physics, Applied)We investigated the combined effect of flux pinning by three-directional columnar defects (CDs) in a wide field-angular range of YBa Cu
Cu Oy thin films, where CDs parallel to the
Oy thin films, where CDs parallel to the  -axis and CDs crossing at
-axis and CDs crossing at 
 (
( =45
=45 , 60
, 60 and 80
and 80 ) relative to the c-axis were installed by 200 MeV Xe-ion irradiations. The three-directional CDs with
) relative to the c-axis were installed by 200 MeV Xe-ion irradiations. The three-directional CDs with 

 60
60 form a field angular curve of critical current density Jc with a broad peak centered at magnetic field (B) parallel to the
form a field angular curve of critical current density Jc with a broad peak centered at magnetic field (B) parallel to the  -axis, whereas the Jc shows no peaks around the crossing angles of
-axis, whereas the Jc shows no peaks around the crossing angles of 
 . When the crossing angle is expanded to
. When the crossing angle is expanded to  =
= 80
80 , a drastic change in the field- angular behavior of Jc is induced: there is not a large enhancement of
, a drastic change in the field- angular behavior of Jc is induced: there is not a large enhancement of  around B//c. We also demonstrated that the combined configuration consisting of CDs at
around B//c. We also demonstrated that the combined configuration consisting of CDs at  = 0
= 0 ,
,  45
45 ,
,  60
60 and
and  80
80 provides a uniform enhancement of
provides a uniform enhancement of  over a wide angular-region.
over a wide angular-region.
Amekura, Hiroshi*; Toulemonde, M.*; Narumi, Kazumasa*; Li, R.*; Chiba, Atsuya*; Hirano, Yoshimi*; Yamada, Keisuke*; Yamamoto, Shunya*; Ishikawa, Norito; Okubo, Nariaki; et al.
Scientific Reports (Internet), 11(1), p.185_1 - 185_11, 2021/01
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:75.03(Multidisciplinary Sciences)We report the track formation of 10 nm in diameter in silicon irradiated with 6 MeV C , i.e., much lower energy than the previously reported energy threshold.
, i.e., much lower energy than the previously reported energy threshold.
 Fe
Fe O
O
Ishikawa, Norito; Taguchi, Tomitsugu*; Kitamura, Akane; Szenes, G.*; Toimil-Molares, M. E.*; Trautmann, C.*
Journal of Applied Physics, 127(5), p.055902_1 - 055902_7, 2020/02
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:44.34(Physics, Applied)Hillock formation is one of the important aspects of radiation-induced modification of solid material. To our knowledge this is first result showing that the hillock formation in ceramics is affected by the velocity effect. The present result include Se-dependences of hillock dimensions based on precise measurement using TEM (transmission electron microscopy). The paper should be published to make researchers aware that hillock size is actually comparable to ion-track size in wide Se range. In addition, the results include important insight about the hillock formation mechanism of ceramics irradiated with swift heavy ions.
 with swift heavy ions; TEM study
with swift heavy ions; TEM studyIshikawa, Norito; Okubo, Nariaki; Taguchi, Tomitsugu
Nanotechnology, 26(35), p.355701_1 - 355701_8, 2015/09
Times Cited Count:30 Percentile:74.62(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)In this study, CeO was irradiated with 200 MeV Au ions at oblique incidence. Observation of as-irradiated samples by transmission electron microscope (TEM) shows that hillocks are created not only at the wide surfaces, but also at the crack faces of the thin samples. Since the hillocks created at the crack faces can be imaged by TEM, their shape and crystallographic features can be revealed. From the images of hillocks created at the crack faces, many of the hillocks are found to be spherical. We present a first experimental evidence that hillocks created for CeO
was irradiated with 200 MeV Au ions at oblique incidence. Observation of as-irradiated samples by transmission electron microscope (TEM) shows that hillocks are created not only at the wide surfaces, but also at the crack faces of the thin samples. Since the hillocks created at the crack faces can be imaged by TEM, their shape and crystallographic features can be revealed. From the images of hillocks created at the crack faces, many of the hillocks are found to be spherical. We present a first experimental evidence that hillocks created for CeO irradiated with swift heavy ions have a crystal structure whose lattice spacing and orientation coincide with those of the matrix. The mechanism of spherical crystalline hillock formation is discussed based on the present results.
irradiated with swift heavy ions have a crystal structure whose lattice spacing and orientation coincide with those of the matrix. The mechanism of spherical crystalline hillock formation is discussed based on the present results.
Futakawa, Masatoshi
IOP Conference Series; Materials Science and Engineering, 74(1), p.012001_1 - 012001_7, 2015/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:65.6(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Innovative researches using neutrons are being performed at the Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility, MLF, at the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex, J-PARC, in which a mercury target system is installed for MW-class pulse spallation neutron sources. The structural materials of the mercury target are subjected to irradiation damage due to protons and neutrons, very high cycle fatigue damages due to repeated pressure waves caused by the proton beam bombardment in mercury and so-called liquid metal embrittlement. That is, the structural materials must be said to be exposed to the extremely severe environments. In the paper, research and development relating to the material issues in the high power spallation neutron sources that has been performed so far at J-PARC is summarized.
Nordlund, K.*; Sand, A. E.*; Granberg, F.*; Zinkle, S. J.*; Stoller, R.*; Averback, R. S.*; Suzudo, Tomoaki; Malerba, L.*; Banhart, F.*; Weber, W. J.*; et al.
NEA/NSC/DOC(2015)9 (Internet), 86 Pages, 2015/00
Within this report, we review the current understanding of primary radiation damage from neutrons, ions and electrons with emphasis on the range of validity of the dpa concept in all main classes of materials, and in particular discuss known shortcomings. We recognise that the current NRT-dpa standard is fully valid in the sense of a scaled radiation exposure measure, as it is essentially proportional to the radiation energy deposited per volume. As such, it is highly recommended to be used in reporting neutron damage results to enable comparison between different nuclear reactor environments and ion irradiations. However, in the sense of a measure of damage production the NRT-dpa value has several well-known problems. We discuss this matter and propose an improved dpa definition.
 revealed by
revealed by  O-NMR
O-NMRTokunaga, Yo; Nishi, Tsuyoshi; Nakada, Masami; Ito, Akinori*; Sakai, Hironori; Kambe, Shinsaku; Homma, Yoshiya*; Honda, Fuminori*; Aoki, Dai*; Walstedt, R. E.*
Physical Review B, 89(21), p.214416_1 - 214416_8, 2014/06
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:31.93(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The magnetic phase transition near 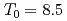 K in AmO
K in AmO has been investigated microscopically by means of
has been investigated microscopically by means of  O NMR. To avoid complexities arising from sample aging associated with the alpha decay of
O NMR. To avoid complexities arising from sample aging associated with the alpha decay of  Am, all measurements have been performed within 40 days after sample synthesis. Even during such a short period, however, a rapid change of NMR line shape has been observed at 1.5 K, suggesting that the ground state of AmO
Am, all measurements have been performed within 40 days after sample synthesis. Even during such a short period, however, a rapid change of NMR line shape has been observed at 1.5 K, suggesting that the ground state of AmO is very sensitive to disorder. We have also confirmed the loss of
is very sensitive to disorder. We have also confirmed the loss of  O NMR signal intensity over a wide temperature range below
O NMR signal intensity over a wide temperature range below 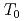 , and more than half of oxygen nuclei are undetectable at 1.5 K. This behavior reveals the persistence of slow and distributed spin fluctuations down to temperatures well below
, and more than half of oxygen nuclei are undetectable at 1.5 K. This behavior reveals the persistence of slow and distributed spin fluctuations down to temperatures well below 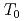 . In the paramagnetic state, strong NMR line broadening and spatially inhomogeneous spin fluctuations have been observed. The results are all indicative of short-range, spin-glass-like character for the magnetic transition in this system.
. In the paramagnetic state, strong NMR line broadening and spatially inhomogeneous spin fluctuations have been observed. The results are all indicative of short-range, spin-glass-like character for the magnetic transition in this system.
Nemoto, Yoshiyuki; Miwa, Yukio; Kaji, Yoshiyuki; Tsukada, Takashi
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 343(1-3), p.313 - 317, 2005/08
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:24.22(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The aim of this work is to evaluate corrosion behavior of irradiated materials these would be used in spallation neutron sources. Solution annealed high purity Fe-18Cr-12Ni specimens were used in this study. Ni , H+ and He
, H+ and He ions were irradiated at 473 to 773K. After corrosion procedure, the specimens were examined with atomic force microscope (AFM) to evaluate corrosion behavior. It was shown that the corroded volume of irradiated area increased with radiation damage. Higher H content at lower temperature accelerated corrosion, but H at higher temperature did not accelerate corrosion. He suppressed corrosion, and corroded volume was larger for the specimens irradiated at higher temperature than these at lower temperature. It is suggested from this study that H and He affect the corrosion behavior of irradiated alloy.
ions were irradiated at 473 to 773K. After corrosion procedure, the specimens were examined with atomic force microscope (AFM) to evaluate corrosion behavior. It was shown that the corroded volume of irradiated area increased with radiation damage. Higher H content at lower temperature accelerated corrosion, but H at higher temperature did not accelerate corrosion. He suppressed corrosion, and corroded volume was larger for the specimens irradiated at higher temperature than these at lower temperature. It is suggested from this study that H and He affect the corrosion behavior of irradiated alloy.
Konishi, Satoshi*; Kimura, Akihiko*; Akiba, Masato; Nakamura, Hiroo; Nagasaka, Takuya*; Muroga, Takeo*; Hasegawa, Akira*; Matsui, Hideki*
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi, 46(5), p.311 - 322, 2004/05
no abstracts in English
Nemoto, Yoshiyuki; Miwa, Yukio; Tsuji, Hirokazu; Tsukada, Takashi
Nihon AEM Gakkai-Shi, 11(4), p.242 - 248, 2003/12
no abstracts in English
Nishijima, Toshiji*; Hearne, S. M.*; Jamieson, D. N.*; Oshima, Takeshi; Lee, K. K.; Ito, Hisayoshi
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 210, p.196 - 200, 2003/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:12.51(Instruments & Instrumentation)The radiation damage in silicon carbide (SiC) schottky diode was studied using ion beam induced current (IBIC). Schottky diodes with electrodes of 30  m on n- or p-type 6H-SiC were fabricated using the evaporation of Al, Ni, and Au. To study the radiation damage of diodes, the 2MeV-He ion micro beam with a diameter of 1
m on n- or p-type 6H-SiC were fabricated using the evaporation of Al, Ni, and Au. To study the radiation damage of diodes, the 2MeV-He ion micro beam with a diameter of 1  m was irradiated from 10
m was irradiated from 10 to 10
to 10 /cm
/cm into a 10
into a 10  m
m  10
10  m area. As the result, the value of IBIC decreased with increasing the dose of 2 MeV-He. This indicates that the charge collection decreases by the recombination centers introduced by irradiation.
m area. As the result, the value of IBIC decreased with increasing the dose of 2 MeV-He. This indicates that the charge collection decreases by the recombination centers introduced by irradiation.
Kamiya, Tomihiro; Oikawa, Masakazu*; Oshima, Takeshi; Hirao, Toshio; Lee, K. K.; Onoda, Shinobu*; Laird, J. S.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 210, p.206 - 210, 2003/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:12.51(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
Ando, Masami; Tanigawa, Hiroyasu; Jitsukawa, Shiro; Sawai, Tomotsugu; Kato, Yudai*; Koyama, Akira*; Nakamura, Kazuyuki; Takeuchi, Hiroshi
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 307-311(Part1), p.260 - 265, 2002/12
Times Cited Count:39 Percentile:90.08(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Kikuchi, Kenji
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi, 44(8), p.622 - 623, 2002/08
no abstracts in English
Nishijima, Toshiji*; Oshima, Takeshi; Lee, K. K.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 190(1-4), p.329 - 334, 2002/05
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:58.11(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
Tsukada, Takashi
Nihon Yosetsu Kyokai "Genshiryoku Kozo Kiki No Zairyo, Sekkei, Seko, Kensa Ni Kansuru Koshukai" Tekisuto, 40 Pages, 2002/00
no abstracts in English